Climate changes and sudden, unpredictable heavy rain deluges are impacting the control of surface water, with drainage channel systems becoming a crucial element for infrastructure. Such systems are designed to quickly and effectively remove surface water from a variety of application areas to prevent flooding and further building damage.
With over 30 years of experience, SABdrain is your partner for drainage solutions. A range of products in various roads, railways, airports, construction, façades and architectural applications. Our range includes high strength cast iron, architectural stainless, durable galvanised & reinforced stone grates to suit SABdrain polypropylene channels.
SABdrain is the official Australasian distributor of Jonite; a manufacturer of innovative and eco-friendly decorative, reinforced stone and bespoke architectural products.
Types of Drainage Systems
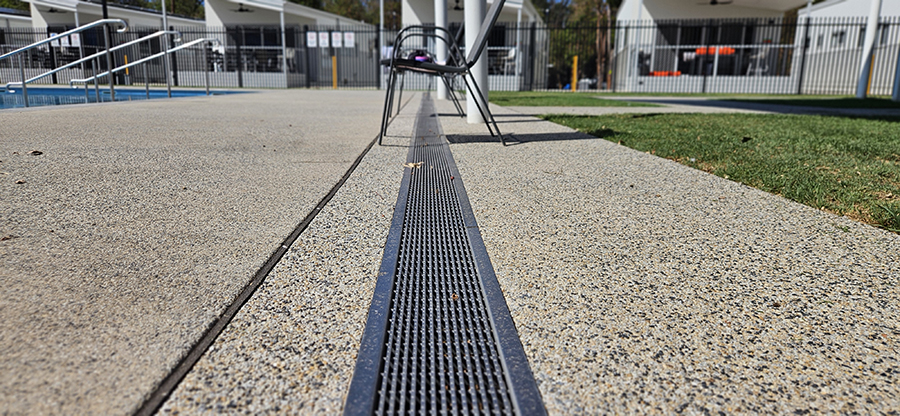
Linear Trench Drainage
Linear drains feature a long, narrow channel that collects and diverts water away from the surface. These drains are often made of materials such as stainless steel, polymer concrete, or PVC, and can be customized in terms of size, depth, and grate design to suit your needs. Usually, several channels are joined to create a ‘run’ of drainage – collecting, transporting and discharging surface water into sewer networks or other water systems underground.
Advantages of Linear Drains
- Efficient intake, drainage and distribution of water
- Practical maintenance; easy full access with low long-term maintenance costs
- Effective for large catchment areas - cost effective installation
- Range of aesthetic grate options - some adding design value to installation area
Configurations: Constant, Stepped Fall & Sloped
All configurations can achieve efficient drainage and discharge of water. Achieving optimal hydraulic efficiency requires careful planning in the configuration of trench drain systems, also considering the system selected, size and topography of install area.
- Constant DepthThe same size and depth of channel for entire drainage run.
- Stepped FallChannels that successively increase in depth toward the outlet point.
- Incorporating a consistant gradient ensures a steady and sufficient liquid velocity across the entire length of the trench. This approach is particularly useful for long drainage runs, as it reduces the risk of slow-moving water and ensures rapid clearance of surface liquid.
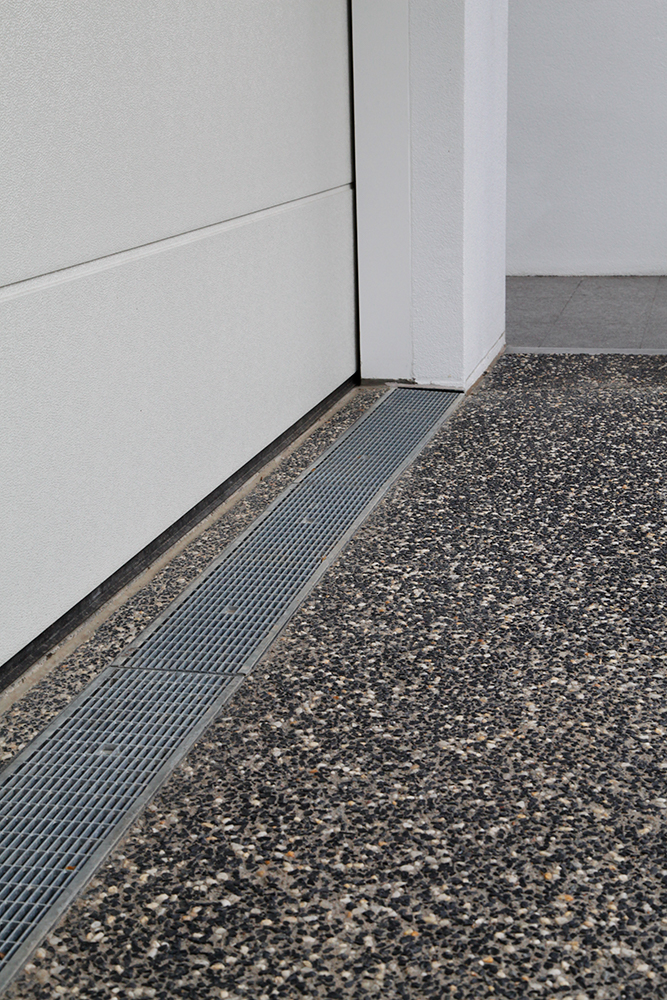
Slot Drains
A slot drain is a type of linear drainage system characterised by its narrow, discreet opening that runs along the surface. Unlike trench drains, slot drains do not have a grated cover; instead they have a slim, elongated slot that allows water to enter the drainage channel below. This design makes slot drains nearly invisible and less obtrusive.
Advantages of Slotted Drains
- Minimalistic slot opening blends seamlessly with the surrounding surface, maintaining a clean and modern look.
- Without grates to clean or replace, slot drains require less frequent maintenance.
- The simple design reduces the risk of debris accumulation and bacterial growth, making it ideal for sanitary environments.
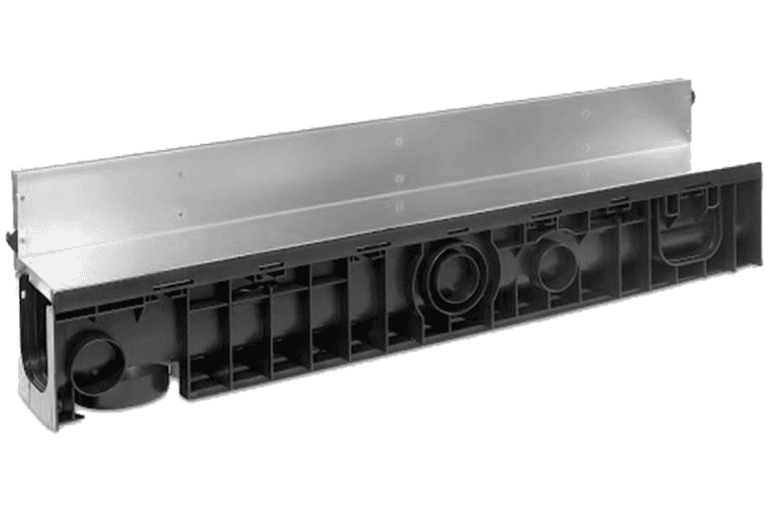
Components of Channel Drainage System
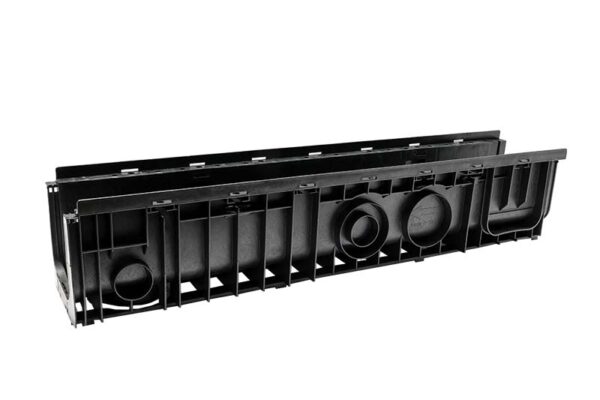
Channel
Trench drainage channels come in a variety of materials, widths and depths. Two main types include the concrete/polymer trench drain and polypropylene, which is what SABdrain channels are made out of.
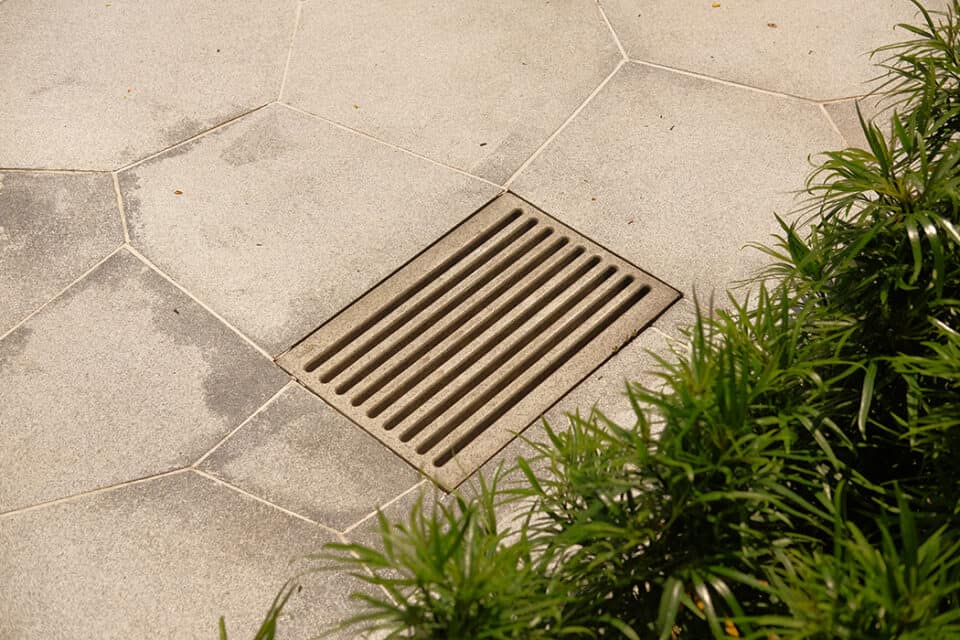
Grates
Grates sit on top of the channel, visible at surface level. They are available in various load ratings, materials and safety features such as anti-slip, lockdown or heel guard.
Channel grates help prevent debris entering the channel, avoiding buildup and blockages.
Factors such as traffic, application area and aesthetics will determine the type of grate used.
Accessories
There are a few accessories you may come across when researching your options for drainage. Most accessories aid with installation or pipe attachment whilst others are for locking down the grate to the channel.
This includes:
- End Caps/End Stops
- End Cap Outlets
- Sprigot Offtakes
- Debris Baskets
- Install Clips
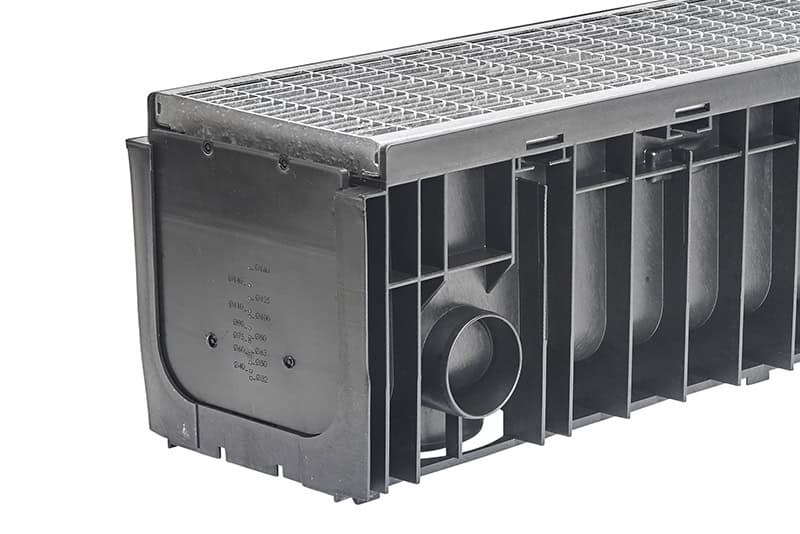

Which is the right channel solution for my project?
Various specifications determine sizing, type and design features for drainage channel, including hydraulic components such as rainfall, gradient and surrounding surface, load class and durability required. A drainage channel for a pedestrian area on a train platform will differ to a system installed in a shopping mall carpark.
- What traffic uses the area?This is critical to ensure your system will not faill. Consider what type of traffic will be travelling over the grate, as well as the weight. Refer to standards such as EN1433 and AS3996. These standards defines load classes with vehicles and application areas.
- Catchment Area & Surface MaterialAccurate hydraulic calculations for sizing and system selection is required.
- AestheticsThe aesthetics of the installation area will affect the chosen grate. Grates, such as Jonite, are available in unique designs and colours; with custom designs available.
- Marine EnvironmentEnvironments which may be corrossive also impact the drainage system chosen. Incorrect specification can lead to dangerous corrosion.




