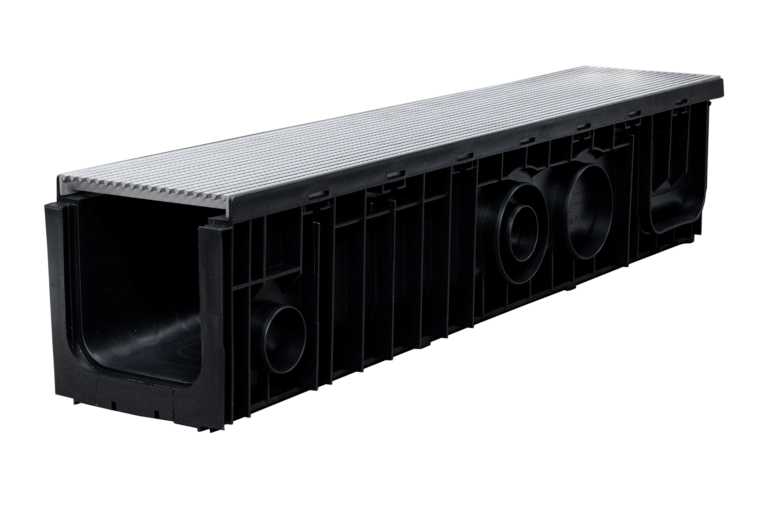
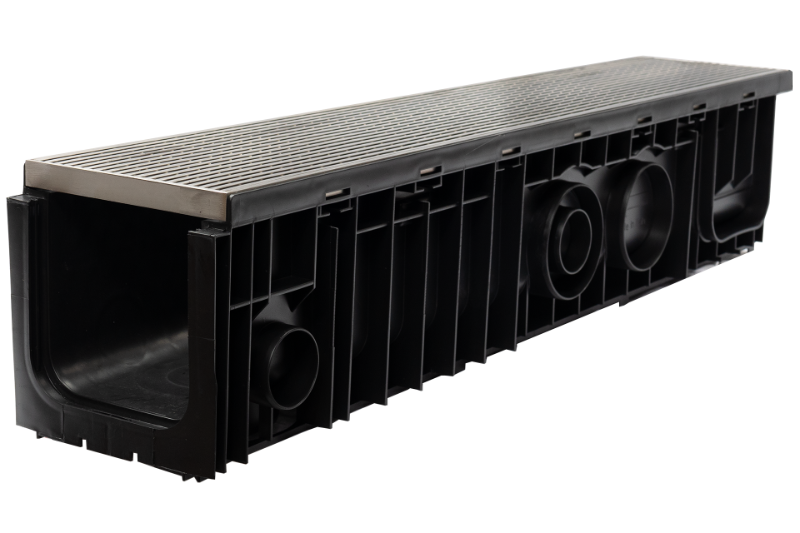
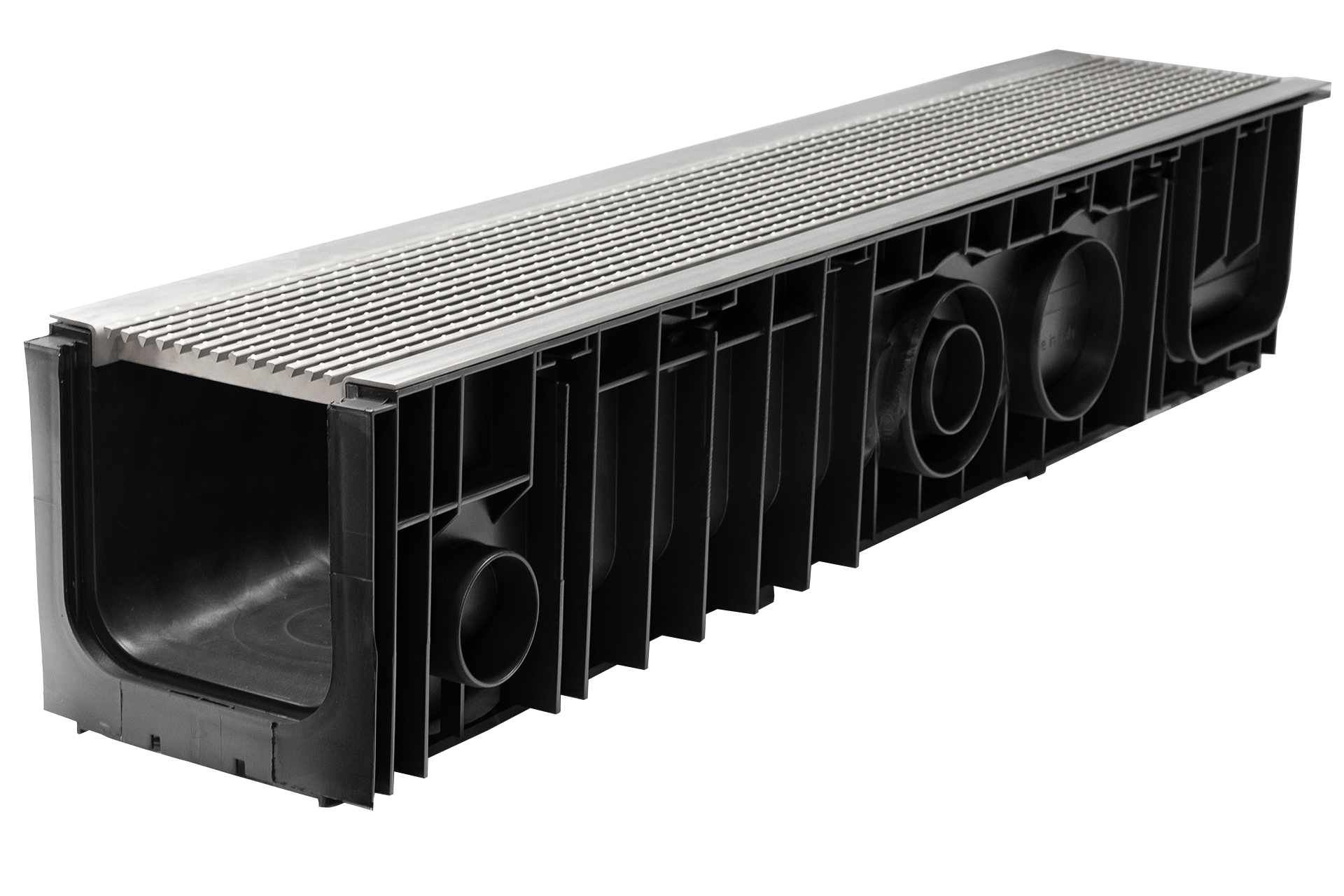
When choosing drainage grates for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, material selection is critical. Stainless steel grates are a popular choice due to their durability, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to corrosion. Among stainless steel options, 304 and 316 grades are the most common. While they share some similarities, the differences between these two materials can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of the drainage system.
What is 304 and 316 Stainless Steel?
Both 304 and 316 stainless steel are austenitic alloys primarily composed of iron, chromium, and nickel. The key distinction lies in their chemical composition, which influences their corrosion resistance and suitability for specific environments.
304 Stainless Steel
Often referred to as “18/8 stainless steel,” 304 contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel. It is widely used across various industries due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
316 Stainless Steel
This grade includes 2-3% molybdenum in addition to chromium and nickel, enhancing its resistance to certain types of corrosion, particularly in harsh environments.
Key Differences between 304 and 316 Stainless Steel
Corrosion Resistance
304 Stainless Steel
Offers excellent resistance to general corrosion and oxidation. However, it may be susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-rich environments, such as coastal areas or pool/spa surrounds.
316 Stainless Steel
The addition of molybdenum improves resistance to chlorides and acids, making it ideal for marine environments, breweries, chemical plants, and areas prone to saltwater exposure.
Cost
304 Stainless Steel
More affordable than 316, making it a practical choice for applications where extreme corrosion resistance is not required.
316 Stainless Steel
Higher in cost due to its superior material properties and molybdenum content, but often justified in environments with corrosive elements.
Strength & Durability
Both grades provide excellent mechanical properties, but 316 stainless steel is slightly stronger due to its molybdenum content.
Appearance
Both materials offer a sleek, polished finish. However, 316 grates may maintain their appearance better over time in corrosive environments, reducing the need for frequent maintenance.
Applications
304 Stainless Steel
Suitable for outdoor spaces with minimal exposure to corrosive elements, such as urban plazas, pedestrian walkways, and garden drainage systems in non-coastal regions.
316 Stainless Steel
Preferred for outdoor applications in harsh environments, such as beachfront promenades, docks, saltwater swimming pools, and industrial sites exposed to chemical runoff or saline water.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Drainage Grate for Your Project
When deciding between 304 and 316 stainless steel grates, consider the following factors:
- Environmental ConditionsIf the installation site is exposed to chlorides or harsh chemicals, opt for 316 stainless steel.
- BudgetFor projects with cost constraints and less exposure to corrosive elements, 304 stainless steel is a reliable choice.
- Long Term PerformanceWhile 316 stainless steel has a higher upfront cost, its superior resistance to corrosion can result in lower maintenance expenses over time.
SABdrain Stainless Options
917
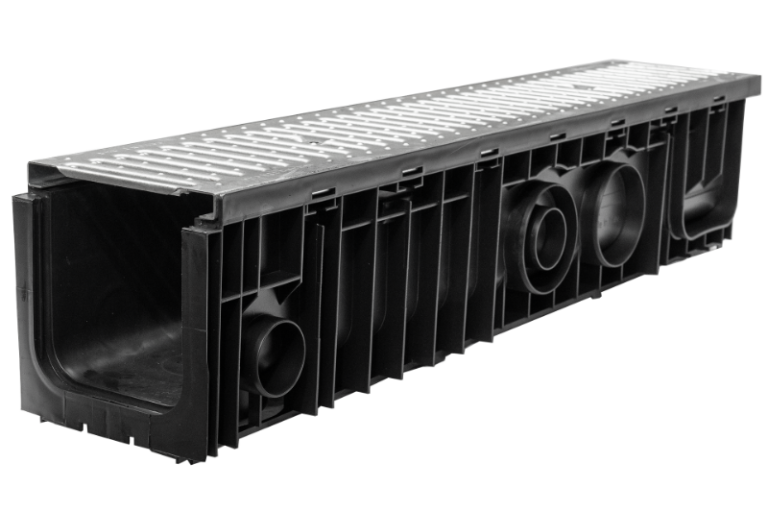

Polypropylene channel with Class A rated 304 stainless steel heel guard grates with antislip nodules.
902
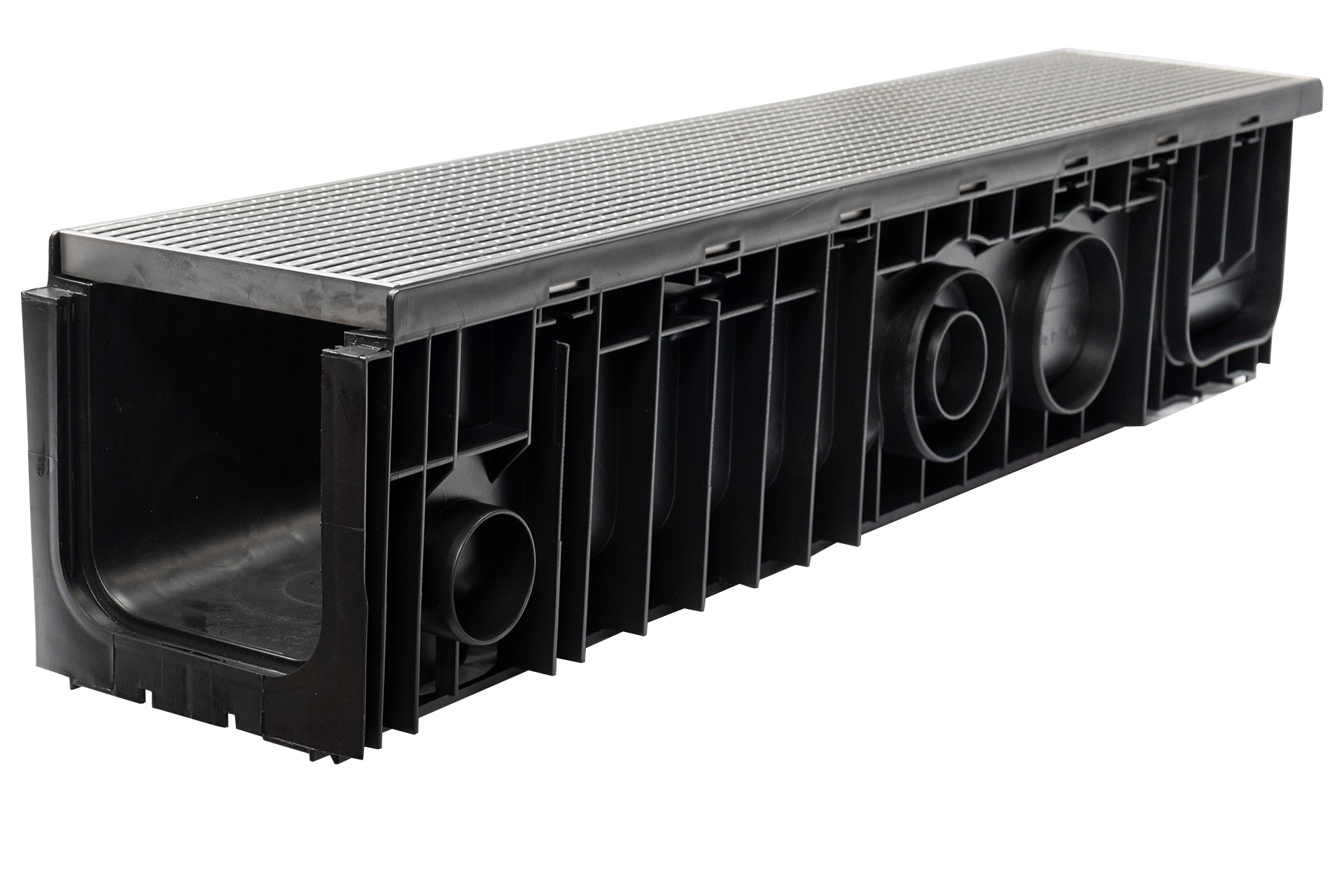

Polypropylene channel with Class A rated 304 stainless steel heel guard grates with antislip nodules.
Understanding the differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel is essential for selecting the right drainage grate for your project. While both offer durability and aesthetic appeal, their distinct properties make them suitable for different applications. By evaluating the environment, budget, and expected lifespan, you can ensure your drainage system remains functional and visually appealing for years to come.
For more guidance on choosing stainless steel drainage grates, feel free to reach out to our team.